2/8, 3/8, 2/24 | Yarn weights for machine knitting
- March 19, 2024
- 1 comments


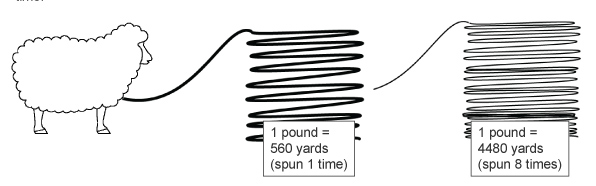


| Symbol | Category | Yarn Types | Yards Per Pound | 4" (10cm) | Machine / Pitch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lace | Lace Fingering 2-ply 10-count crochet thread |
4000 - 10,000 ypp | 33-40 sts | Standard 4.5mm (stranded) | |
| Super fine | Sock Fingering Baby 3-ply |
3000-4000 ypp | 27-32 sts | Standard 4.5mm (stranded) | |
| Fine | Sport Baby 4-ply |
2000-3000 ypp | 23-26 sts | Standard 4.5mm / Double Bed | |
| Light | DK Light worsted |
1000-2000 ypp | 21-24 sts | Mid-Gauge 6.0 |6.5| 7mm/Standard 4.5mm | |
| Medium | Worsted Afghan Aran |
800-1000 ypp | 16-20 sts | Mid-Gauge 6.0 |6.5| 7mm /Bulky 9mm | |
| Bulky | Chunky Craft Rug |
500-800 ypp | 12-15 sts | Bulky 9mm | |
| Super Bulky | Super bulky Roving |
100-500 ypp | 6-11 sts | May not be appropriate. |
© Copyright 2026 Knititnow.com, All rights reserved.